- About
- Network
- Community
- Initiatives
- News
- Events
- Blog
- Publications

CENIC Completes First Backbone Upgrade Allowing Native 400 Gbps Handoffs to CalREN
Categories RENS & NRENS The CENIC Community
Tags calren update
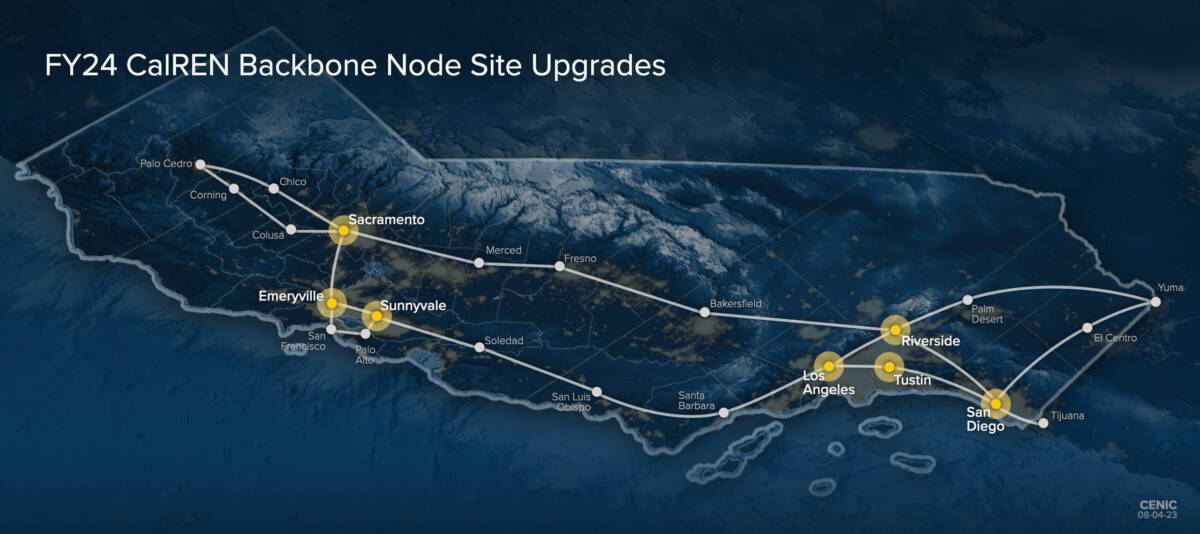
San Diego node site first to be upgraded – six more node sites planned for this fiscal year
During the past several years, CENIC has carried out an ongoing program of upgrades to the California Research and Education Network (CalREN) backbone. Among these upgrades have been capacity increases to coastal and inland backbone routes to 400 Gbps to support advanced optical services such as flex-grid spectrum services, which enable users to send far more data per wavelength with less equipment, power, and rack space.
CENIC also recently announced successful validations of the ZR+ and ZR Bright coherent pluggable optics – without and with integrated amplifiers, respectively – between the Los Angeles and Sunnyvale node sites over the CalREN production network. These validations demonstrated the utility of the latest generation of coherent pluggable optics for big-data applications over long distances.
Now, CENIC is announcing the start of a new phase of its backbone program: the upgrade of major node sites to support native 400 Gbps handoffs from member institutions, beginning with the San Diego node site located at the San Diego Supercomputer Center (SDSC) at UC San Diego. The Sunnyvale, Emeryville, Sacramento, Riverside, Tustin, and Los Angeles node sites are scheduled to be completed through this fiscal year.
Formerly, while the CalREN backbone could support 400 Gbps of data traffic, that traffic could only enter the backbone in 100 Gbps increments. For example, a researcher wishing to send or receive data via 400 Gbps services would have to connect to the CalREN backbone via four 100 Gbps links. With this upgrade to the San Diego backbone node site, a user connected at that site can now simply use one 400 Gbps link.
Frank Würthwein, SDSC Director and Professor in the Department of Physics and at the Halıcıoğlu Data Science Institute at UC San Diego, sees great benefit to the big-data research community in California. “SDSC is excited to work with CENIC on translating innovation into practice. While the first science driver for 400G is experimental particle physics in collaboration with Caltech’s Harvey Newman, we see many other disciplines in the wings, from astronomy to cybersecurity research to genomics to neuroscience, and of course Artificial Intelligence across them all.”
Robert Kwon, CENIC Vice President of Engineering, further highlighted the importance of doing more with less. “With this series of upgrades, CENIC can deliver cost-efficient and higher bandwidth connections for both the CalREN backbone and member connections. As always, CENIC remains committed to creating a high-performance yet power-efficient network that our members and the world needs.”
As well as supporting researchers through making high-capacity handoffs possible, these upgrades also ensure that CalREN can scale significantly in the future. Instead of each 100 Gbps of traffic occupying one physical port at a backbone node site, each port can now accept 400 Gbps of traffic. This frees up ports that can be used to connect other users as well as continuing CENIC’s history of moving significantly more data with much less equipment, rack space, and power.
"These new native 400Gbps handoffs, along with the panoply of services that CENIC currently offers — Layer2 Virtual Private Network Services, Optical Services, and Optical Spectrum Services — will further pre-position one of the world’s leading research communities with additional cyberinfrastructure tools to continue a remarkable history of scientific and medical innovations," said CENIC’s President and CEO, Louis Fox.
Related blog posts
Pacific Wave Signs MoU with New Japan-Based Research and Education Exchange Facility FUJIXP
Pacific Wave, International Networks at Indiana University (IN@IU), and Coalition of Interoperable Networks for Japan (CINJI) and International have signed an MoU formalizing connectivity to FUJIXP, CINJI's new Tokyo-based open exchange facility for research and education networks.
The Big Game Is Big Data: How CENIC and the California Research and Education Network Support Member Athletics
When Fresno State needed to connect to Pac-12 Enterprises to broadcast a live football game over CBS, the Chancellor's Office reached out to CENIC for what Pac-12 later called the smoothest turn-up they've ever experienced.


