- About
- Network
- Community
- Initiatives
- News
- Events
- Blog
- Publications
Network Overview
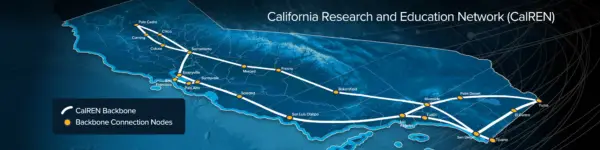
CENIC's California Research and Education Network (CalREN) is a multi-tiered, advanced network-services fabric serving the majority of research and education institutions in the state. The CalREN backbone includes roughly 8,000 miles of CENIC-owned and managed fiber, last-mile fiber, and hundreds of optical components.
Reaching out from the CalREN backbone, thousands of circuits purchased at bulk rates on behalf of our members and managed by CENIC penetrate every part of California, connecting more than 12,000 schools, colleges, universities, libraries, and other research and cultural organizations. As shown on the above map, all of these endpoints are connected to CalREN either directly or via intermediate “aggregation” sites, such as main libraries and county offices of education, which provide connectivity to CalREN for other endpoints through their own connection.
A Three-Tiered Network
In addition to providing the entire California research and education community with the most cost-effective advanced services network available, the multitiered CalREN infrastructure supplies high-level network services needed to successfully conduct high-performance research activities. It also provides network researchers in California with the infrastructure needed to conduct critical investigations into optical networking technology.
Three independent networks operate simultaneously over CalREN:
CalREN-DC:
CENIC's Digital California network provides high-quality network services for students/teachers/staff and for faculty, researchers, and staff at education institutions. Connectivity to the commercial Internet is provided by this tier. All CENIC Charter Associates are connected to this tier.
CalREN-HPR:
CENIC's High-Performance Research network provides leading-edge services for large-application users at CENIC Associates sites. Connectivity to Internet2 is provided by this network tier.
CalREN-XD:
CENIC's eXperimental/Developmental network tier consists of a set of build-to-order resources to support bleeding-edge services for network researchers at sites such as the San Diego Supercomputer Center, the University of California Institutes for Science and Innovation, the Center for Advanced Computing Research at Caltech and its Jet Propulsion Laboratory, the University of Southern California and its Information Sciences Institute, Stanford University and the Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, national laboratories, and other major network research entities that collaborate with these researchers in California.
Latest Network Upgrades
CENIC engineers perform regular upgrades at the three network layers outlined below. Recent network upgrades include:
Layer 1: Optical Backbone
- Upgraded the coastal path between LA and Sunnyvale to flexible grid technology in support of planned 400G+ backbone upgrades
- Added colorless, directionless, contentionless (CDC) capabilities to the coastal path to extend software provisioning to the optical layer
- Completed new fiber path in northern California between Corning and Sacramento. New fiber path adds diversity for Corning and includes two new optical nodes in Chico and Palo Cedro
- Extend flexible grid and CDC capabilities to the Inland route traversing Oakland, Sacramento, Fergus, Fresno, Bakersfield, and Riverside (FY 23)
- Initial deployment of SmartOptics metro optical solution to provide additional peering capacity up to 500 Gbps and distances up to 40 km
Layer 2: (DC/HPR access, commodity peering transport, Pacific Wave)
- Upgraded the Pacific Wave backbone between Los Angeles and Sunnyvale to 1x300G, leveraging CENIC’c flexible grid capabilities over the coastal path (FY23)
- Upgrade of the Pacific Wave backbone capacity between Los Angeles, Sunnyvale, and Seattle to 400G (FY23)
- Upgrade the WRN backbone between Los Angeles, El Paso, Albuquerque, Denver, Chicago, and Seattle to 100G+
- Availability of MPLS based L2 solution, ELAN, and ELINE, to provide a more robust and seamless L2 connection
- Migration of current L2 circuits to MPLS based L2 solutions
Layer 3: Routed Networks (DC and HPR backbones)
- Deployed Segment Routing MPLS across the backbone to support flexible MPLS services
- Consolidation of DC and HPR platforms to provide additional flexibility in associate connectivity and location
- Consolidation of DC and HPR backbone links to 4x100G to enable more efficient use of available backbone bandwidth (FY22)
- Upgrade of backbone aggregation routers at major hub sites to support 400Gbps connection (FY22)
- Upgrade of 400G capable backbone aggregation router at Triangle Court and San Diego (FY22)
- Upgrade of higher density 100G capable DC backbone aggregation router at Fresno, Fergus, Sacramento, San Francisco, and San Luis Obispo (FY22)
- Implementation and deployment of enhanced network architectures and features (Route Reflector, Next-Hop Self, BGP PIC, TI-LFA) for quicker restoration of services (FY22)

